Introduction
Loguytren problems refer to a condition that affects the connective tissues in the body, primarily the hands. It is a progressive disorder that leads to the thickening and tightening of tissue beneath the skin, resulting in the bending of fingers. Often misunderstood, Loguytren problems can cause discomfort, limited mobility, and a significant impact on daily life.
Understanding this condition is essential as it enables early diagnosis and effective management. Loguytren problems typically develop over time, with symptoms becoming more noticeable in middle-aged and older individuals. While the exact cause remains unknown, various factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and medical conditions, contribute to its onset.
Addressing Loguytren problems requires a multi-faceted approach that includes medical treatment, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. In this article, we will delve deeper into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options for managing Loguytren problems effectively.
What Are Loguytren Problems?
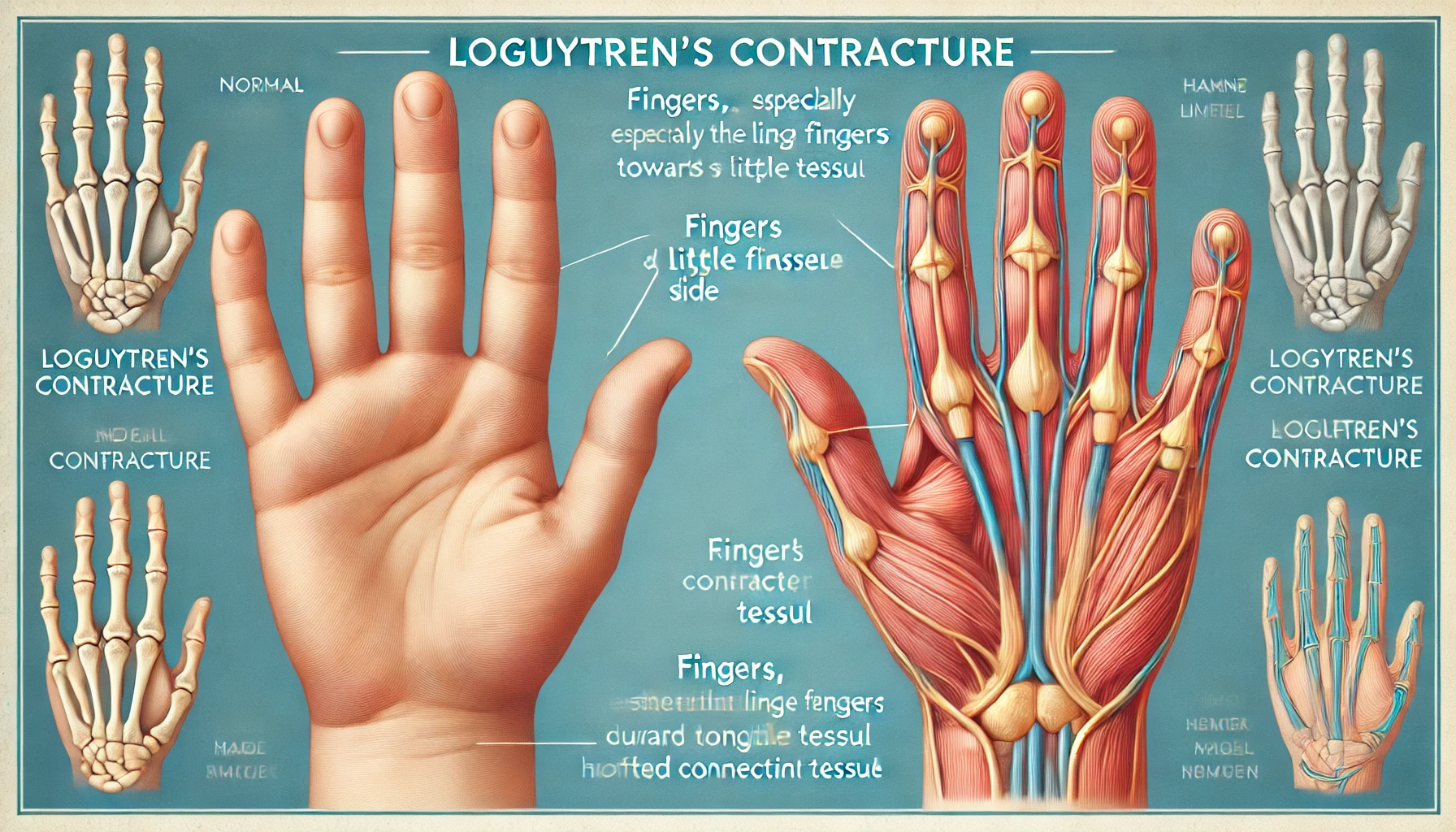
Loguytren problems, also known as Loguytren’s contracture, affect the fascia—a layer of tissue under the skin. This condition causes the fingers, especially the ring and little fingers, to bend inward towards the palm. Over time, it becomes difficult to straighten the fingers, leading to restrictions in hand movements.
The development of Loguytren problems is gradual, often taking years before severe symptoms appear. Early on, individuals may notice lumps or nodules forming in the palm. These nodules are usually painless but can become firm over time. As the disease progresses, thickened tissue forms bands that pull the fingers inward, making simple tasks such as gripping objects, shaking hands, or typing more challenging.
Despite its impact, Loguytren problems are not considered life-threatening. However, they can significantly affect the quality of life, particularly for those who rely on manual dexterity for their profession or daily activities. Understanding its progression helps individuals seek timely medical intervention and explore suitable treatment options.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Loguytren problems remains unknown, but research suggests that genetic and environmental factors play a significant role in its development. Studies indicate that individuals with a family history of Loguytren problems are more likely to develop the condition.
Age and gender are also key risk factors, with men over the age of 40 being more susceptible than women. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, epilepsy, and liver disease, have been linked to an increased risk of developing Loguytren problems. Lifestyle factors, including excessive alcohol consumption and smoking, may also contribute to the condition’s progression by affecting blood circulation and connective tissue health.
Occupational hazards and repetitive hand movements have been debated as potential contributors to Loguytren problems. However, there is no direct evidence linking manual labor to the onset of the disease. Individuals experiencing early symptoms should monitor changes in hand function and seek medical advice to assess their risk factors.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
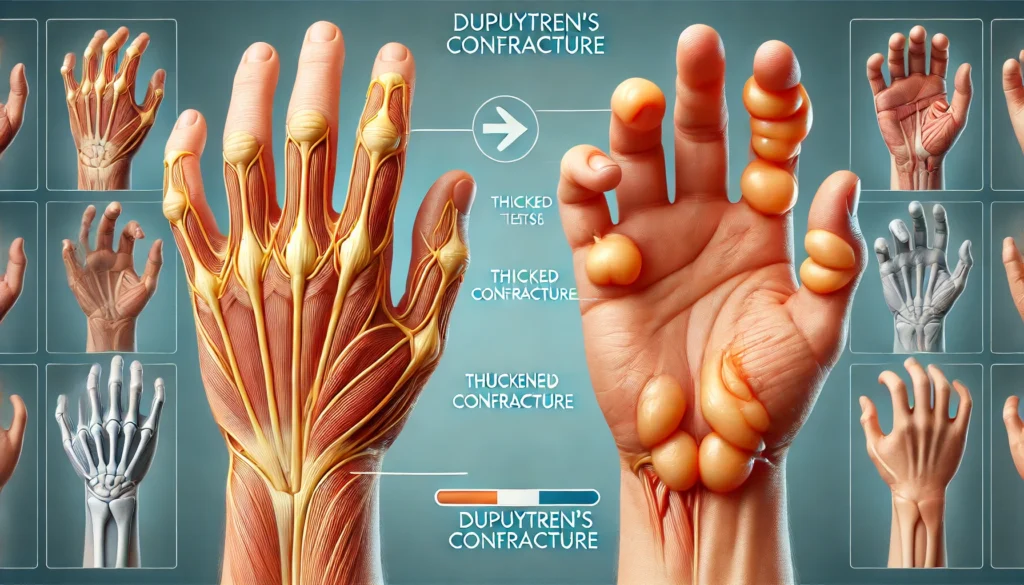
Loguytren problems manifest in stages, beginning with the formation of small lumps or nodules in the palm. These nodules may feel tender initially but usually become firm and painless over time. As the condition progresses, the skin in the affected area may appear puckered or dimpled.
One of the most noticeable symptoms is the gradual bending of the fingers towards the palm. The ring and little fingers are most commonly affected, though other fingers may also be involved. This contracture makes it difficult to perform everyday tasks such as holding objects, shaking hands, or typing.
Diagnosing Loguytren problems typically involves a physical examination by a doctor. The “tabletop test” is a common diagnostic method, where the patient attempts to place their hand flat on a surface. If they cannot fully extend their fingers, it suggests the presence of Loguytren problems. Additional imaging tests are rarely needed, as the condition can be diagnosed based on clinical signs.
Treatment Options and Management
There is no definitive cure for Loguytren problems, but various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve hand function. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and its impact on daily life.
Non-surgical approaches include physical therapy, stretching exercises, and corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation. While these methods may slow progression, they do not reverse contractures. For moderate to severe cases, medical interventions such as enzyme injections (collagenase clostridium histolyticum) are used to break down thickened tissue.
Surgical procedures, such as fasciectomy or needle aponeurotomy, are recommended for advanced cases where fingers become severely bent. These procedures help restore mobility by removing affected tissue. However, post-surgery rehabilitation, including physical therapy and hand exercises, is crucial for long-term success.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Adjustments
While Loguytren problems cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk of progression. Maintaining overall hand health through regular stretching exercises can help improve flexibility and reduce stiffness.
Diet and nutrition also play a role in managing connective tissue health. A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports collagen production and reduces inflammation. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can also improve blood circulation and tissue health.
For those at risk, regular hand massages and using ergonomic tools may help minimize strain on the fingers. Staying proactive about hand function and seeking early medical advice can make a significant difference in managing Loguytren problems effectively.
Living with Loguytren Problems: Coping Strategies
Living with Loguytren problems can be challenging, especially as the condition progresses. Individuals may experience difficulty performing simple tasks such as buttoning clothes, holding utensils, or using a computer keyboard. Adapting daily activities through assistive tools, such as grip-friendly utensils and ergonomic keyboards, can ease the strain on the hands.
The psychological impact of Loguytren problems should not be overlooked. Many individuals experience frustration and emotional distress due to their inability to perform routine tasks. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, occupational therapists, or support groups can help individuals cope with these challenges.
Maintaining a positive mindset and staying informed about treatment advancements can empower individuals to manage their condition effectively. Connecting with others facing similar challenges can also provide motivation and valuable insights for living with Loguytren problems.
Conclusion
Loguytren problems, though not life-threatening, can significantly impact hand function and overall quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential for early intervention and effective management.
While there is no guaranteed cure, various medical and lifestyle interventions can slow the progression and improve mobility. Seeking medical advice at the first sign of symptoms can lead to better outcomes and prevent severe contractures.
By staying proactive, individuals can continue to lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by Loguytren problems. Ongoing research and advancements in treatment offer hope for improved management and potential new therapies in the future.
FAQs
What is Loguytren’s contracture?
Loguytren’s contracture is a hand condition where the connective tissue under the skin thickens, causing fingers (usually the ring and little fingers) to bend inward towards the palm.
What causes Loguytren problems?
The exact cause is unknown, but genetic factors, age, gender, and certain medical conditions (like diabetes and liver disease) may contribute. Lifestyle factors like smoking and alcohol consumption can also increase the risk.
What are the early symptoms of Loguytren’s contracture?
Early symptoms include small lumps or nodules in the palm, thickened skin, and mild finger stiffness. Over time, the fingers may bend permanently.
Is Loguytren’s contracture painful?
In most cases, Loguytren’s contracture is not painful. However, some people experience tenderness in the nodules or discomfort as the condition progresses.
How is Loguytren’s contracture diagnosed?
A doctor can diagnose Loguytren’s contracture through a physical examination. The “tabletop test” (placing the hand flat on a surface) helps determine the severity of finger contracture.
Can Loguytren’s contracture be cured?
There is no permanent cure, but treatments like enzyme injections, physical therapy, or surgery can improve hand function and slow progression.
When should I consider surgery for Loguytren’s contracture?
Surgery is recommended if the fingers become significantly bent, interfering with daily tasks. A doctor will assess the severity and suggest the best approach.
Can exercise help with Loguytren’s contracture?
Stretching exercises and physical therapy may help maintain hand flexibility in the early stages but won’t reverse severe contractures.
Is Loguytren’s contracture hereditary?
Yes, genetics play a role. If a close family member has Loguytren’s contracture, the risk of developing it is higher.
What are the latest treatments for Loguytren’s contracture?
New treatments include collagenase injections, radiation therapy, and minimally invasive surgical techniques. Research is ongoing for improved therapies.